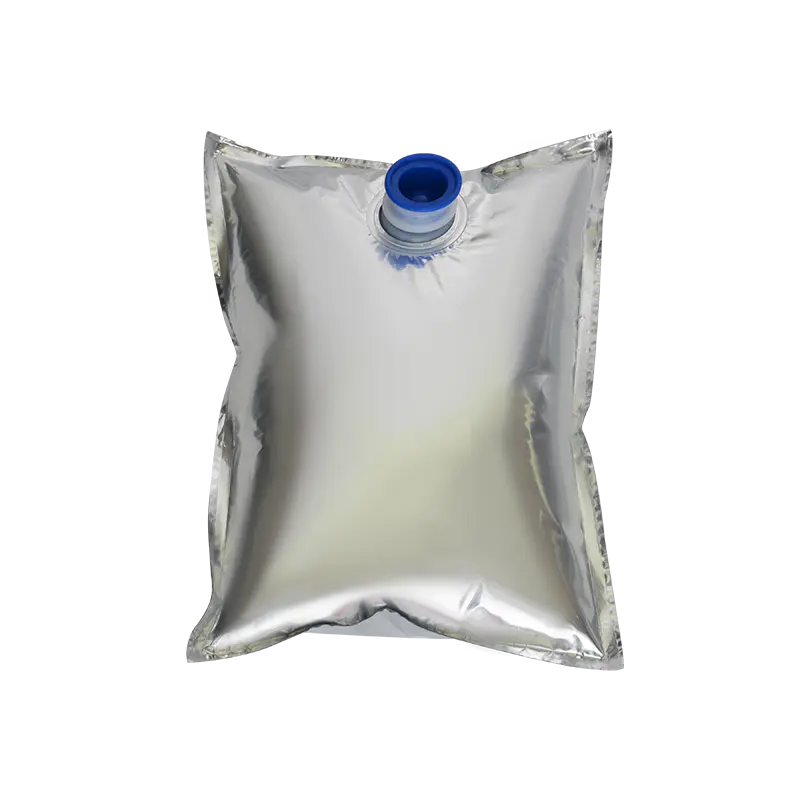
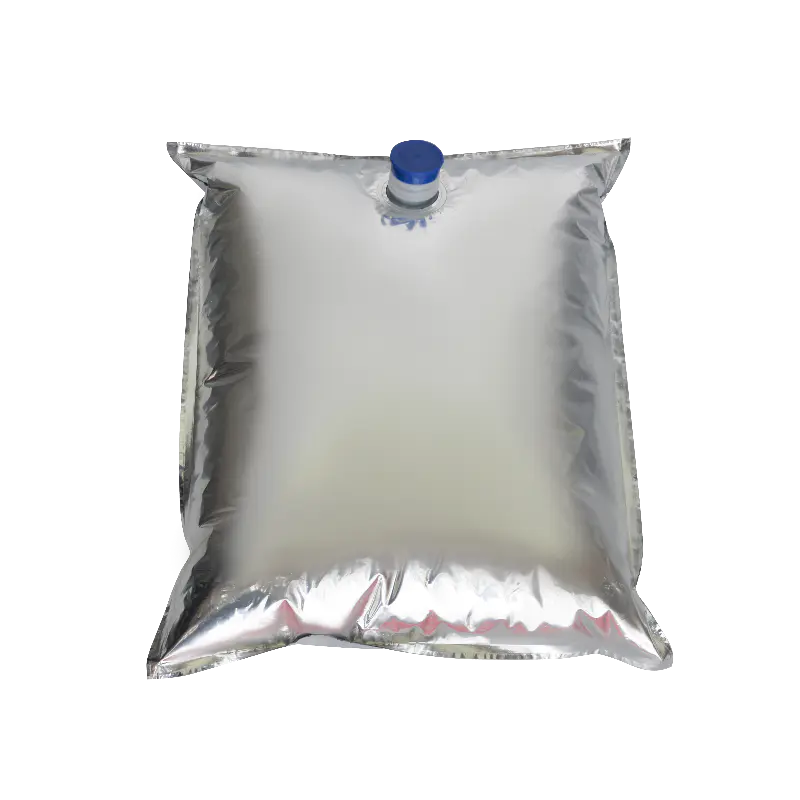
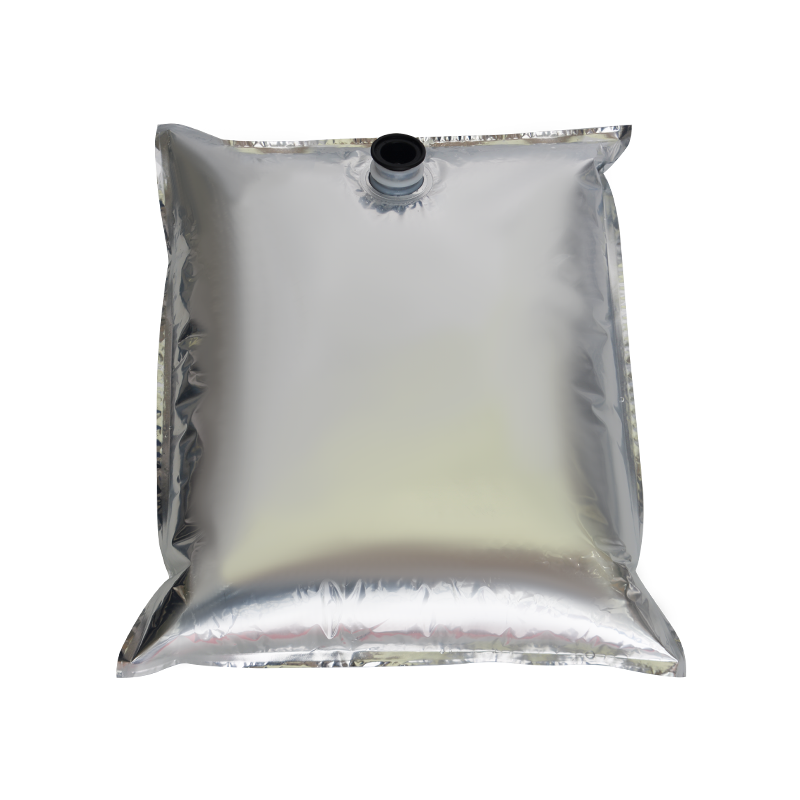
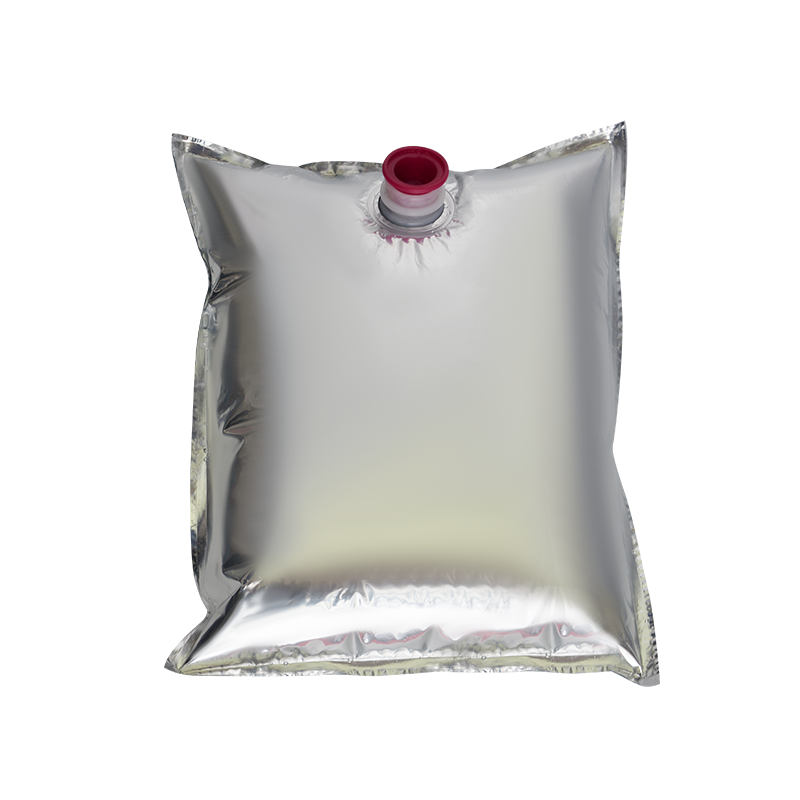
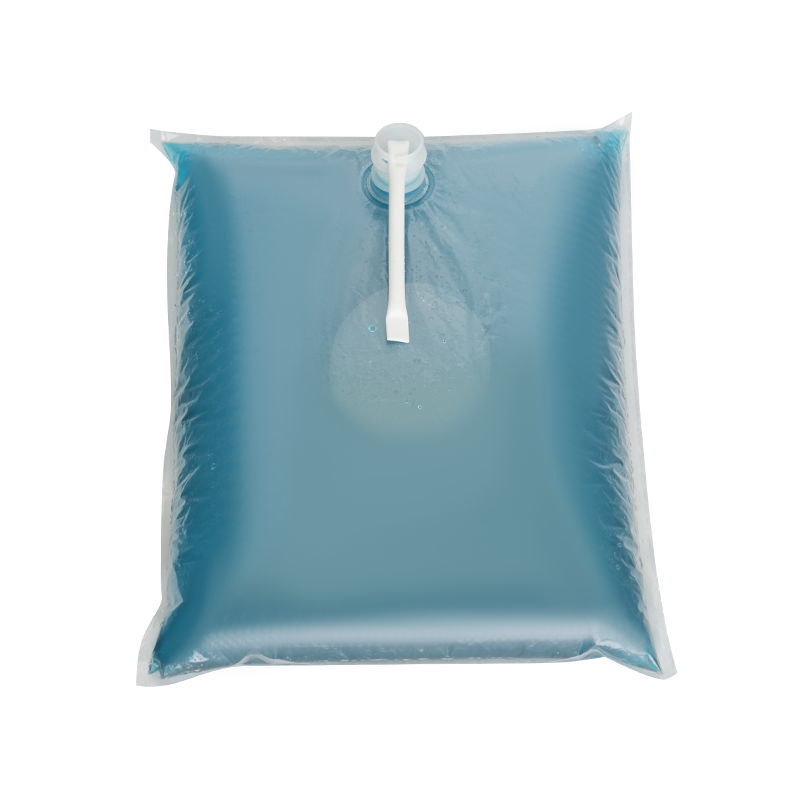
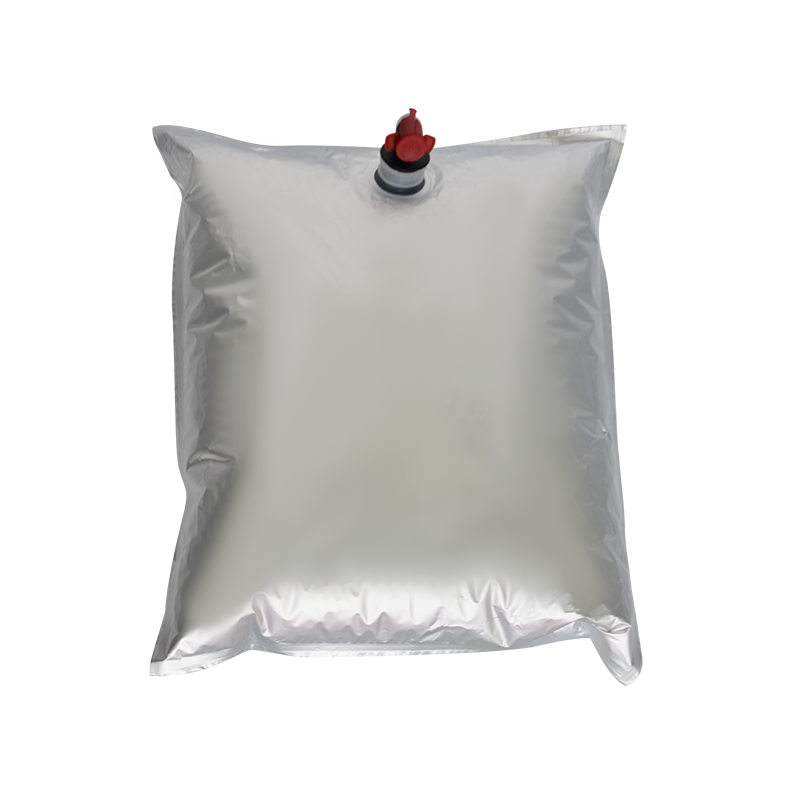
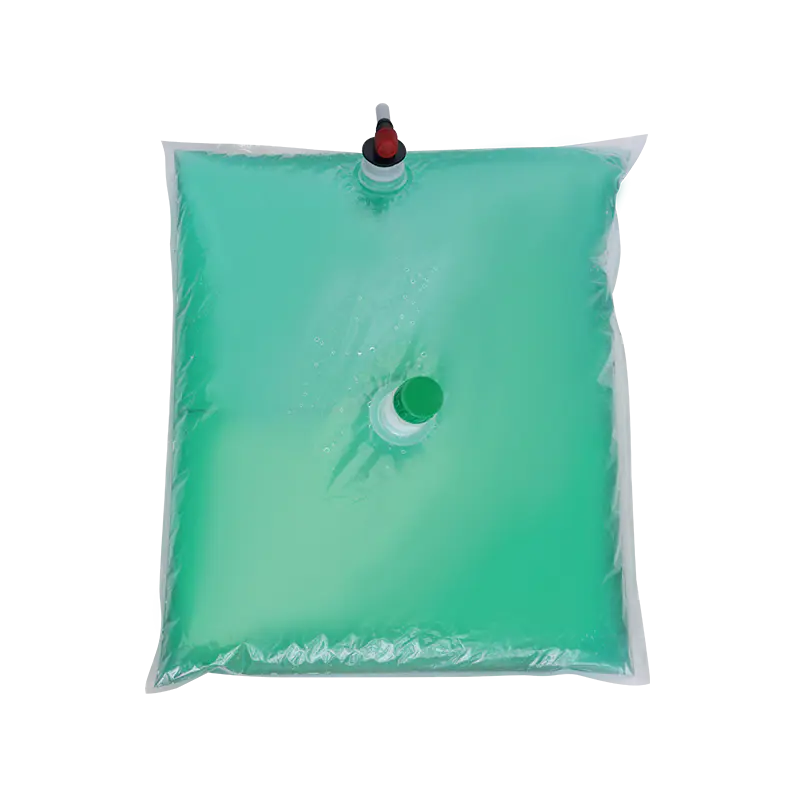
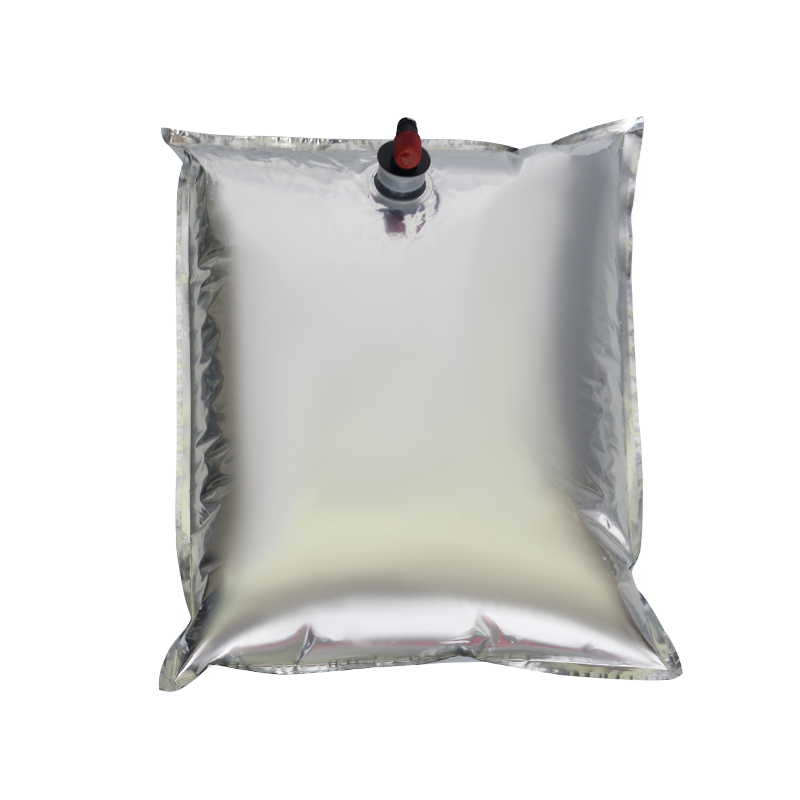
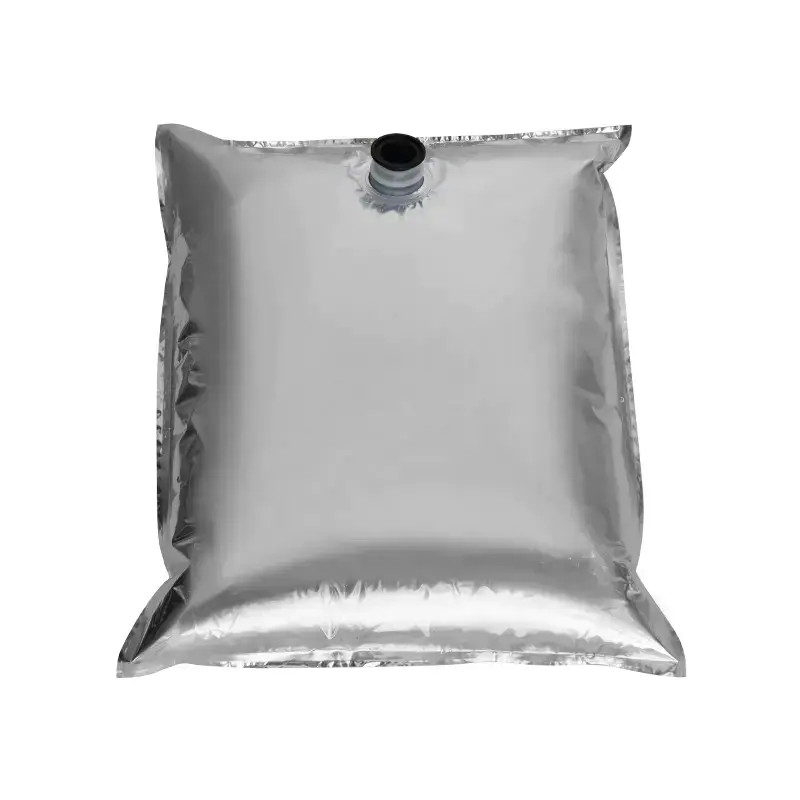
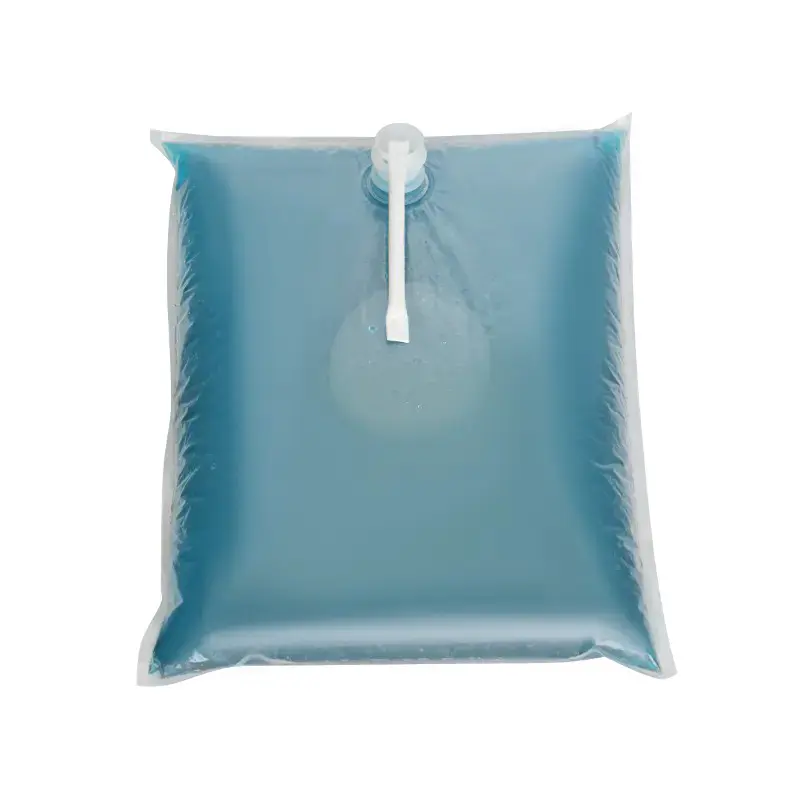
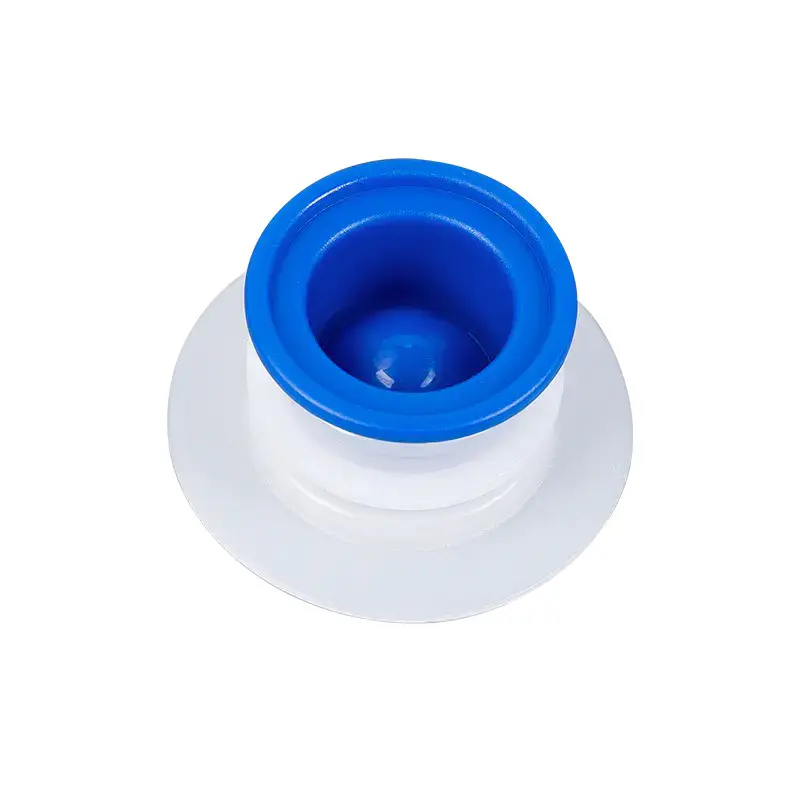
In modern liquid packaging, Bag-in-Box (BIB) packaging has been widely adopted in industries such as food and beverage, daily chemicals, and pharmaceuticals due to its lightweight, environmentally friendly, and space-efficient design. Within the entire BIB packaging system, the Bag In Box Liquid Valve, as the critical component connecting the interior of the package with external access, directly determines the storage safety, ease of use, and shelf life stability of liquid products, making it a key indicator of BIB packaging quality.
I. Core Functions and Industry Value of the Bag-in-Box Liquid Valve
The BIB liquid valve is more than a simple fluid channel; it is a functional component that integrates sealing protection, precise flow control, and contamination resistance. From a functional perspective, its primary role is to ensure the tightness of liquids during storage and transportation. Whether it's retaining carbon dioxide in carbonated beverages or preventing leaks in high-viscosity sauces, the valve's sealing performance is directly related to whether product quality meets standards. During the dispensing process, valves must provide on-demand flow control, preventing splashing and waste during pouring while also adapting to flow requirements in different scenarios. For example, both bulk filling in the catering industry and small-scale dispensing at home require stable flow regulation.
From an industry perspective, high-quality Bag-in-Box Liquid Valve can significantly enhance the market competitiveness of bag-in-box packaging. For food and beverage companies, the valve's corrosion and aging resistance can extend product shelf life and reduce losses caused by packaging issues. For the daily chemical and pharmaceutical industries, the valve's hygienic design prevents liquids from coming into contact with external contaminants during the dispensing process, meeting stringent industry hygiene standards. As consumers demand more convenient packaging, easy-to-open and easy-to-close valve design has become a crucial factor influencing user experience and brand reputation.

II. Key Technical Parameters and Design Considerations of Bag-in-Box Liquid Valve
When evaluating the performance of a Bag-in-Box Liquid Valve, several key technical parameters require special attention. Sealing pressure is a key performance indicator. High-quality valves must maintain a complete seal within a certain pressure range to prevent leakage caused by transport shock or ambient temperature fluctuations. Furthermore, the valve's fluid resistance must be kept within a reasonable range to ensure smooth and unimpeded liquid access. Especially for high-viscosity liquids (such as syrups and lubricants), the design of the valve's internal passages must fully consider fluid dynamics to minimize flow resistance.
In terms of design, the Bag-in-Box Liquid Valve must balance practicality and adaptability. Food-grade applications typically utilize materials such as polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) that meet food contact safety standards. Some high-end applications also incorporate silicone seals to enhance sealing performance. For chemical or corrosive liquids, more corrosion-resistant engineering plastics are used. In terms of structural design, currently mainstream valves often utilize "push-to-open" or "twist-to-open" mechanisms for ease of operation. Some valves also feature leak-proof latches to ensure a tight seal when not in use, preventing leakage due to misoperation.
The connection between the valve and the bag-in-box also requires stability. Common connection methods include heat seals and snap-fit connections. Heat seals achieve a seamless fit between the valve and the bag, providing a superior seal. Snap-fit connections facilitate valve replacement and maintenance, making them suitable for applications requiring frequent use. Regardless of the connection method used, the joints must be robust to prevent detachment or leakage during use.
III. Industry Application Trends and Selection Recommendations for Bag-in-Box Liquid Valves
With the continuous expansion of the bag-in-box packaging market, the application scenarios for bag-in-box liquid valves are also becoming increasingly specialized, demonstrating a trend toward specialization and multifunctionality. In the food and beverage industry, valves for carbonated beverages require higher pressure-resistant sealing performance to prevent carbon dioxide loss that affects taste. For liquids stored at low temperatures (such as freshly squeezed juices and dairy products), valves must be low-temperature resistant to prevent material embrittlement and seal failure at low temperatures. In the pharmaceutical industry, aseptic valve design is a key priority. Some high-end products utilize disposable, sterile valves to prevent contamination during drug handling. For businesses, selecting the appropriate Bag-in-Box Liquid Valve requires a comprehensive consideration of both product characteristics and application scenarios. The product's physical and chemical properties, such as viscosity, corrosiveness, and gas content, must be clearly defined to determine the valve's material and structural design. Environmental conditions, such as storage temperature, transportation method, and access frequency, must also be considered to ensure the valve's suitability for the intended use. Finally, the valve's compatibility with existing bag-in-box packaging specifications and interfaces must be carefully considered to avoid compatibility issues that could impact packaging efficiency.

As a core component of the bag-in-box packaging system, the performance and design of the Bag-in-Box Liquid Valve directly impact the product's storage, transportation, and user experience. In the context of rapid industry development, businesses must prioritize valve selection and quality control, selecting the right product based on their specific needs. They must also monitor technological innovation and changes in industry standards to enhance the overall competitiveness of their packaging systems and meet market demand for high-quality liquid packaging.

 English
English русский
русский